Harnessing magnetic force to reveal defects!
Precision at its best: Expert MT testing and demagnetization.

Harnessing magnetic force to reveal defects!
Precision at its best: Expert MT testing and demagnetization.
Testing & demagnetization of steel components
From fault detection to complete demagnetization—here’s how it works!
Magnetic particle testing (MT testing) is a trusted method for non-destructive inspection of steel components. It detects fine cracks and material defects invisible to the naked eye, ensuring maximum safety in production. But what comes after testing? Demagnetization is essential to eliminate unwanted residual magnetism. Our advanced technologies provide efficient and reliable demagnetization, ensuring components are ready for seamless processing and optimal performance.
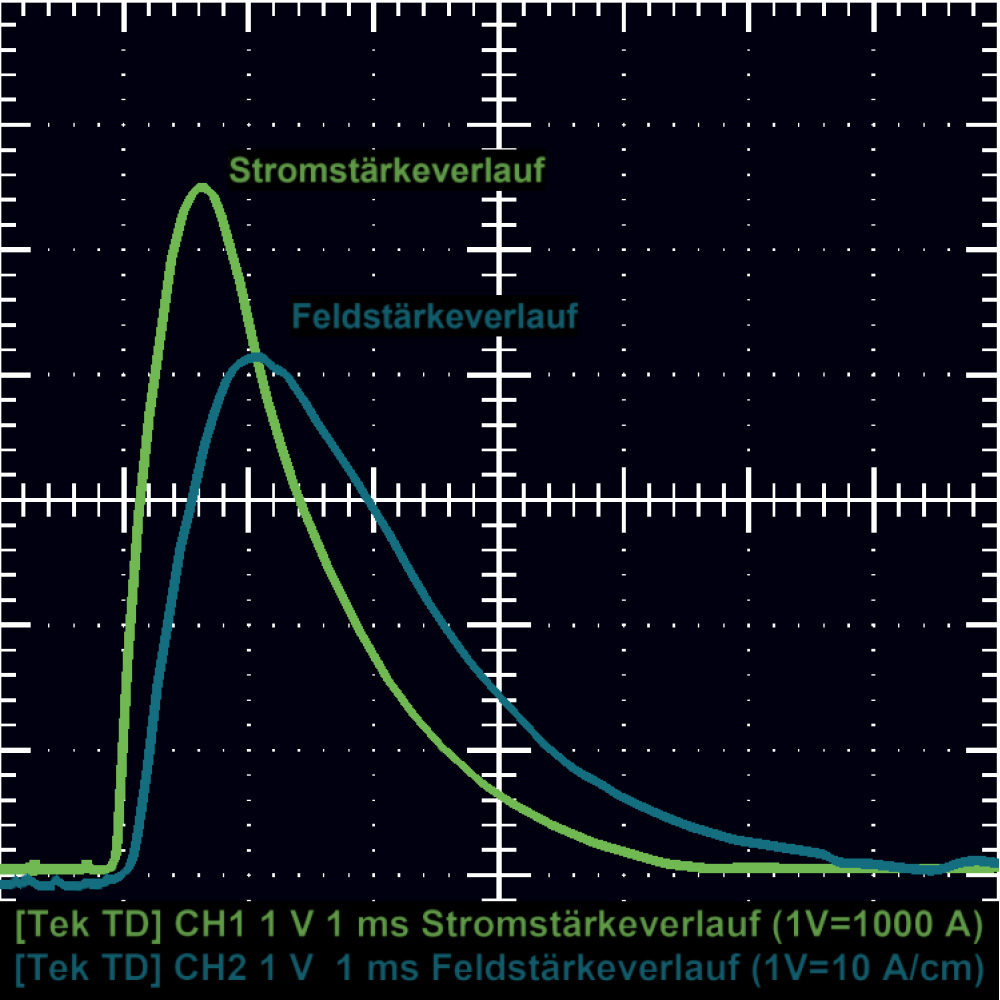
DC pulse technology
Magnetization with DC pulses
Capacitor discharge generates extremely high pulse currents for a few milliseconds. These direct current pulses create magnetic field pulses within the steel components being tested, which emerge as stray fields at surface defects, such as cracks. These stray field pulses exert a powerful, shock-like attraction on the iron oxide particles in the testing medium, causing them to accumulate at the defect sites and become visible under UV illumination.
Users gain the following benefits:
Razor-sharp, clear crack indications
Rapid MT test results in approximately 3 seconds.
High-performance yet compact and lightweight devices with user-friendly operation.
Energy-efficient with minimal operating costs.
Effortless component handling with no need for clamping.
Magnetization with DC pulses
Steel components can be effectively and permanently demagnetized using direct current pulses with decreasing intensity and alternating polarity.
Direct current flow
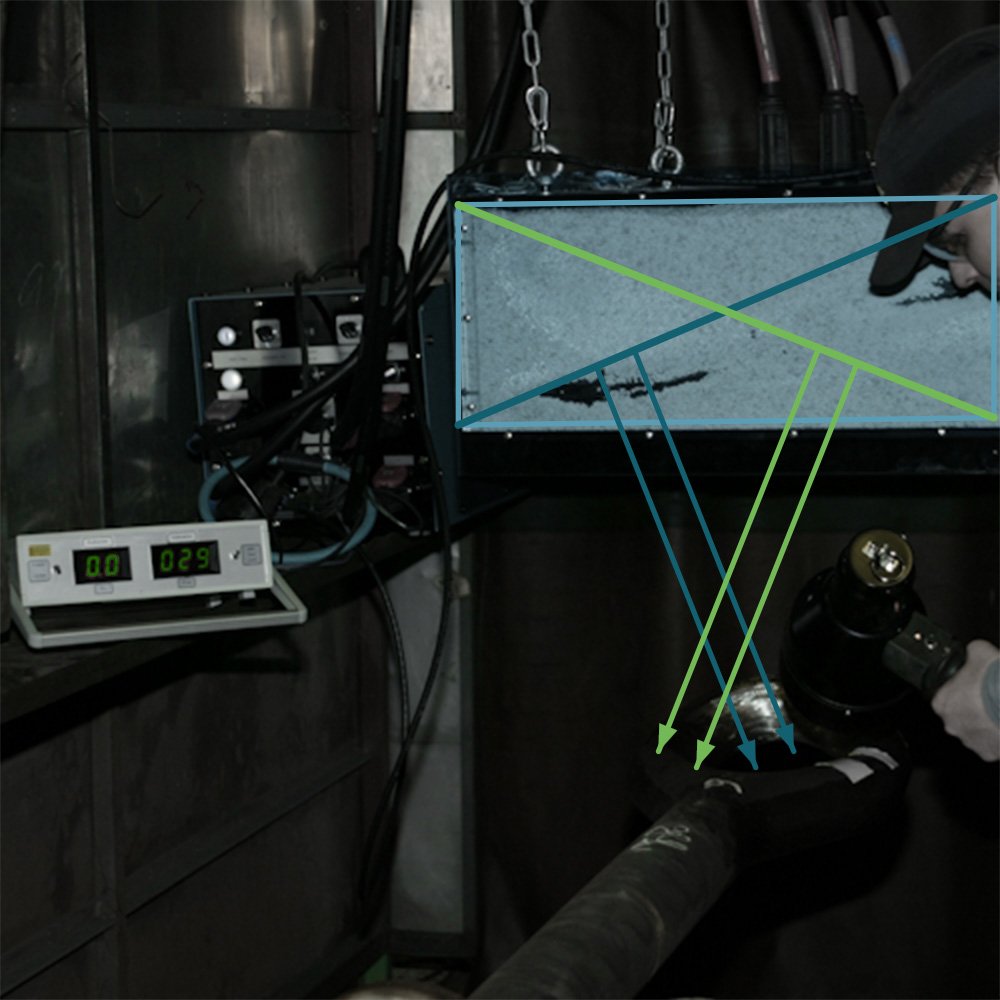
Magnetization using the 4 pole method
In the 4-pole method, test currents flow alternately in a crosswise pattern through the component. The MT test device generates direct current pulses, which are introduced into the component via test cables and magnetic poles, creating magnetic fields along the current paths. Stray fields emerging at crack sites cause a precise accumulation of magnetic powder particles, resulting in clear and well-defined crack indications.
The 4-pole method is ideal for magnetizing flat components and is effectively used for both MT testing and demagnetization.
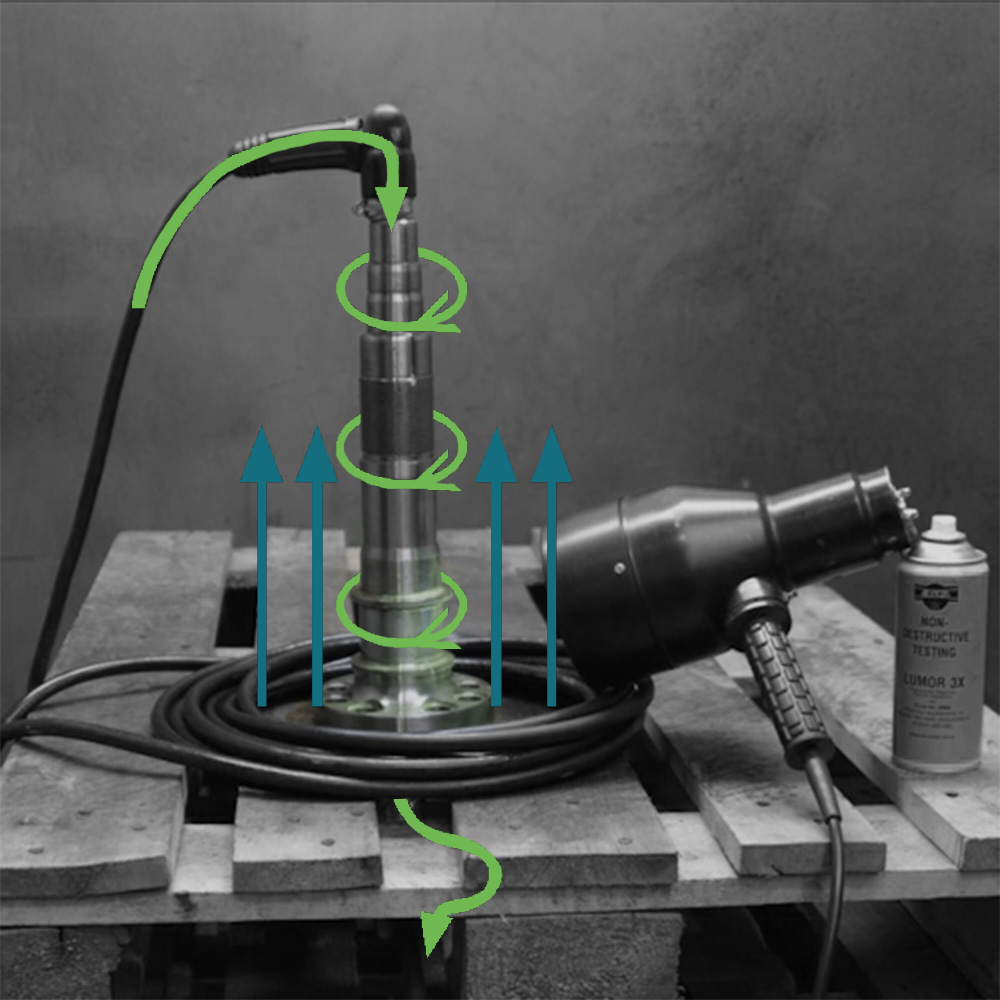


Combined method
Magnetization using the combined method
In the combined method, magnetization is achieved through a combination of direct current flow and coil magnetization. The MT tester generates direct current pulses that alternate between flowing through the component via test cables and magnetic poles or through a coil wound around the component. Stray fields emerging at crack sites cause a precise accumulation of magnetic powder particles, resulting in clear and well-defined crack indications.
The combined method is especially effective for magnetizing rotationally symmetrical components and is utilized for MT testing.
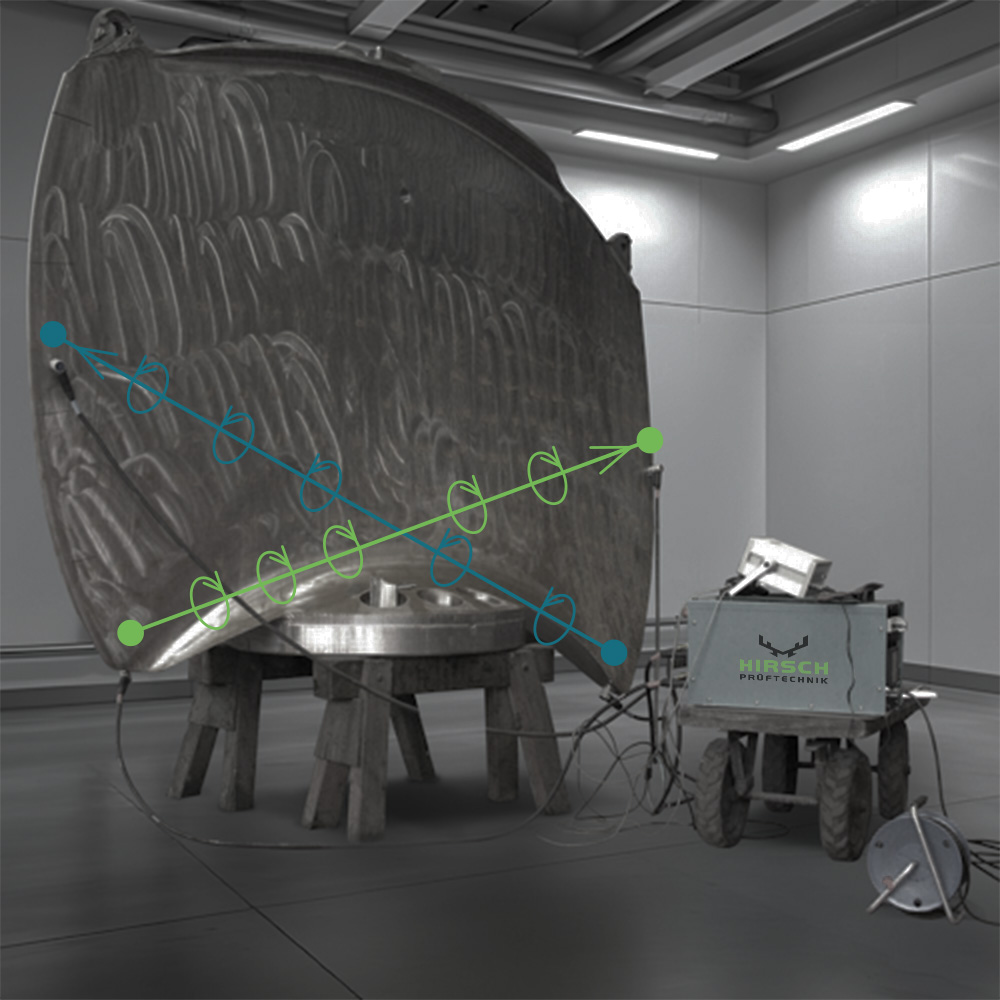
Contact-free method
Dependable crack detection using intersecting magnetic fields.
In the contact-free method, test magnetic fields are generated within two coils positioned at an angle of at least 30° and then introduced into the component. Stray fields emerging at crack sites cause a precise accumulation of magnetic powder particles, resulting in clear and well-defined crack indications. Our MT test table allows for the simultaneous testing and demagnetization of multiple components, efficiently detecting both longitudinal and transverse defects without direct contact.
The contact-free method is ideal for magnetizing compact components with varying geometries and is effectively used for both MT testing and demagnetization.


